Digital Asset Custody


Digital Assets are taking Financial Markets by storm. Whilst the adoption of Digital Assets is on the rise, there has been a lot of volatility recently due to failures of several cryptocurrency players as well as some cryptocurrencies failing to deliver on their value proposition. There is hype that surrounds Digital Assets, especially non-traditional ones, like private coins, art NFT etc.
Despite these factors, Digital Assets remain a very innovative space. The underlying technologies behind Digital Assets, i.e. cryptography, Blockchain and Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) have lots of relevance in Financial Markets across many use cases. Clear examples are CBDC, UOB’s digital bonds issuance using Security Tokens, trade finance and much more.
The financial world envisions unprecedented growth in Digital Assets and Blockchain / DLT to transform the Financial Markets landscape. Fin Techs are moving much faster in this space, creating an ecosystem that banks are equally keen to participate in. To understand Digital Asset Custody, let’s understand what Digital Assets are.
Digital Assets are anything in digital form that have value. It should be possible to establish the ownership of such an asset. Examples of Digital assets in the financial world are Security Tokens, Cryptocurrency, CBDCs, NFTs and many others.
As FI customer base moves towards adopting Digital Assets, there is a strong customer demand to provide services to safeguard these Digital Assets. Digital Assets Custody is a terminology that refers to storing and protecting Digital Assets on behalf of their owners. Essentially, to safeguard the Digital Assets, what needs to be protected are the private keys of customers. This requires usage of sophisticated technologies and appropriate governance to provide the appropriate security and safety.
There have been billions of dollars lost in Digital Asset thefts and hacks. This is where banks have an opportunity to come forward as a trusted partner to help their clients safeguard their Digital Assets for a fee.
Banks have been safekeeping the traditional assets of their customers for a very long time. Our customers who wish to own Digital Assets would like to have peace of mind that their Digital Assets are safe without having to worry about the complicated underlying technologies.
Digital Assets utilise innovative technologies like cryptography and Blockchain / DLT. Assets are created and / or transferred between owners on the Blockchain. Transactions are typically recorded on the Blockchain network itself which can be public or private. Owners have the responsibility to safekeep their cryptographic keys to prove their ownership of assets on the Blockchain network. Losing the keys is equivalent to losing the assets. This also means that private keys become a single point of failure in the system.
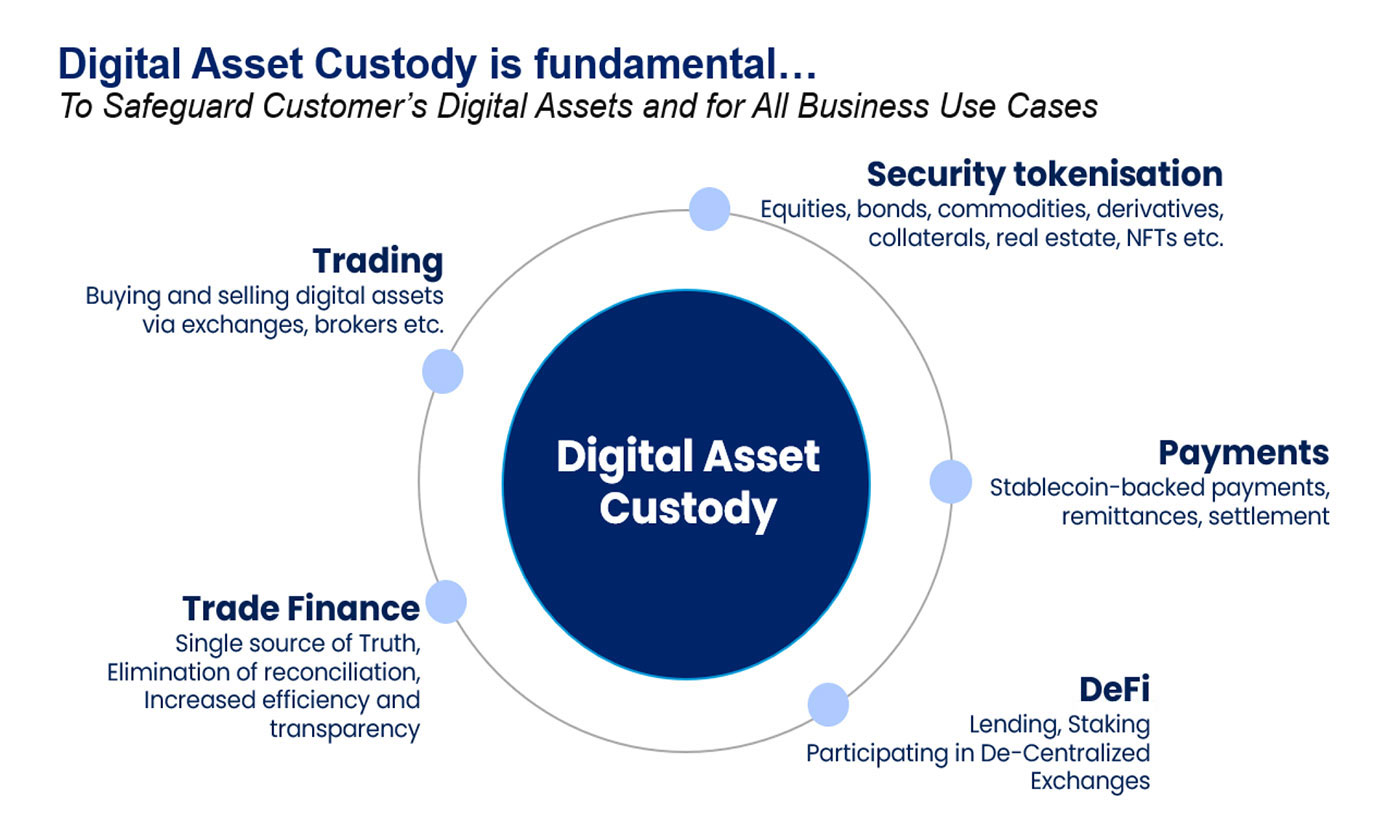
Banks or other FIs can provide DAC service to their customers to safeguard their private keys. As per the figure below, providing Digital Asset Custody Service to clients is a fundamental building block of all Digital Assets use cases, be it trading, payments, DeFi or others. Customers will trust their banks for safeguarding their private keys, thus enabling customers to participate with confidence in the Digital Asset ecosystem.
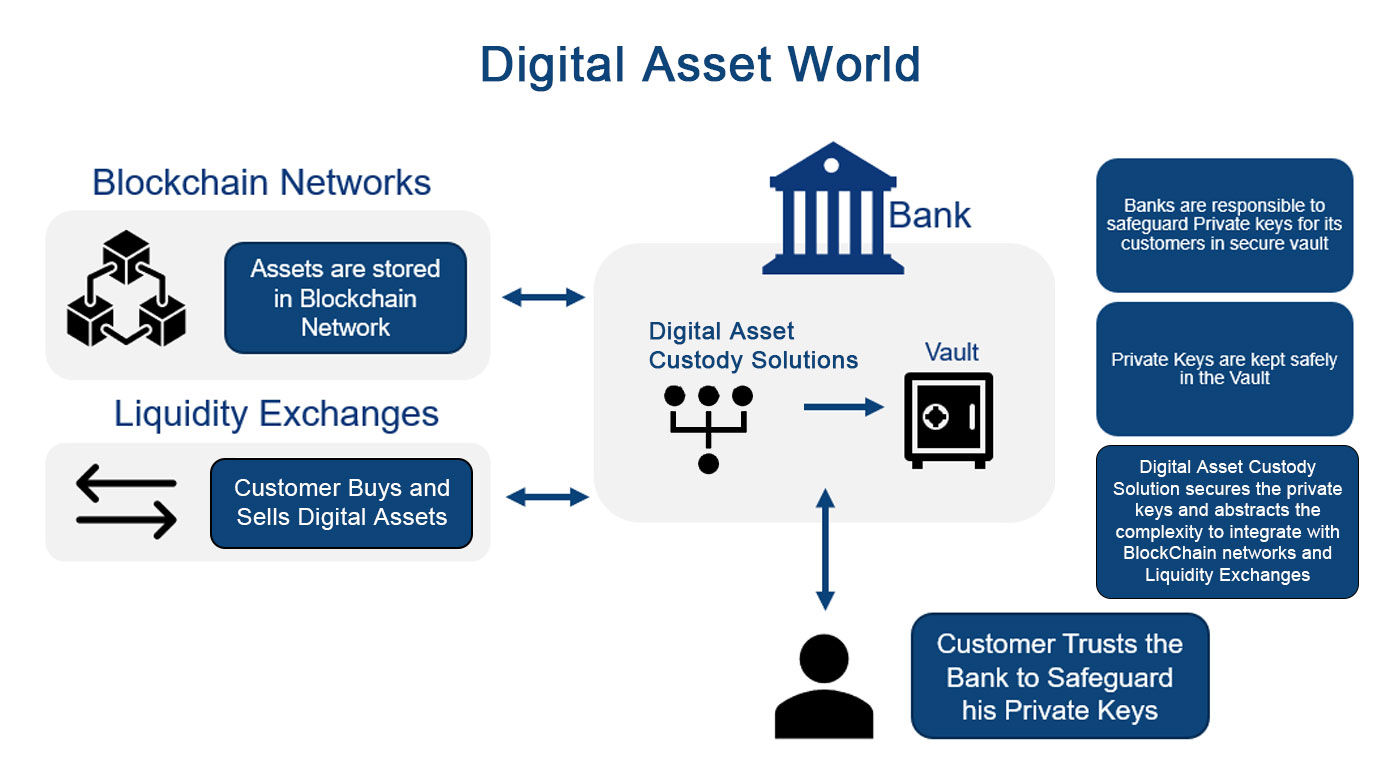
Digital Assets records are usually on the Blockchain network whose ownership is established by private keys. Banks safeguard these private keys in a Digital Asset Custody system usually in a vault. In addition to safeguarding private keys, Digital Asset Custody solution also provides a gateway to connect to rest of the Digital Assets Ecosystem, i.e. Blockchain Networks, Liquidity Exchanges etc.
Digital Assets Custody thus provide a conduit between Traditional banking systems and Digital Assets World as shown below. This helps to abstract the complexity of the new Digital Assets Ecosystem.
Banks as custodians can use a few different methods and combinations to safeguard private keys. The methods provide different options with a tradeoff between security against ease of access and speed of use. On top of this, banks can build their own governance policies according to customer profiles and service offering.
Hot wallets, as the name suggests, are “hot” and ready to use. They are connected to the internet. These are fastest to access for transactions but are the least secure. This approach requires no human involvement, enabling quick transfer of assets which is what certain customers might need, especially for small transactions.
Cold wallets on the other hand are most secure but take time to operate. Usually, they are operated with the help of human involvement. Keys are stored completely offline in a vault and are air gapped. Private key do not come into contact with internet at all, thus providing highest level of security. With the right operational model in place, conducting transactions can take hours to days. Customers can potentially have their own Cold wallets like Ledger or Trezor, but the responsibility of safeguarding the keys is on the customer. When assets size is considerable, it makes sense to get the keys protected by a bank to get institutional grade security for your private keys.
Warm wallets attempt to offer the best of both worlds by keeping the keys in a wallet and implementing an additional process governance layer on top of it which requires approval usually by a human being.
The above choices are usually offered in combination, depending upon the risk profile of the customer and the quantum of Digital Assets that the customer wants to trade. It also depends upon the governance process of the custodian.
As with other Digital Asset regulations, each market is at varying degrees of progress in defining guidelines for Digital Asset Custody. In Asia, markets such as Thailand, Singapore and Hong Kong have already started to sharpen their stance on the approach Financial Institutions should take with themes such as:
As Financial Institutions develop Digital Asset Custody capabilities, they will need to stay up-to-date as Regulations evolve and are implemented in each market. It is expected that regulators will also stipulate certain guidelines on the technology infrastructure design to address the unique needs of Digital Assets. For example, Emphasizing the use of HSM (Hardware Security Module) to store private keys.
As the new Digital Asset World evolves, Digital Custody will be of immense importance to assure customers that their digital assets are safe. Banks or FIs can offer DAC solutions to their clients directly or through a sub-custodian.
Since managing private keys is of utmost importance, providing an in-house custody solution to customers might need significant technology investments and time whereas using a sub-custodian might offer quicker time to market by leveraging their capabilities. Utilizing a sub-custodian also limits the capabilities offered to the profile of the sub-custodian which is a trade-off that banks or FIs needs to evaluate.






